RESEARCH GROUP - STRATIGRAPHIC GEOLOGY
Team:
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| ALDEGA Luca | BRANDANO Marco | CASALBORE Daniele | CHIOCCI Francesco Latino | |
 |
 |
 |
||
| MILLI Salvatore | SANTANTONIO Massimo | SPATOLA Daniele |
Topics:
| Most of the rocks cropping out on the Earth surface were formed through sedimentary processes. Research in sedimentary geology aims at studying sedimentary deposits and processes and at reconstructing paleoenvironment and paleogeography, as well as at defining characters and the subsurface geometries of sedimentary successions, which often host significant georesources (aquifers, hydrocarbons, aggregates, placers). As such, these researches are also relevant to the mitigation of geo-hazards (landslides, sinkholes, local seismic amplification effects etc.). | 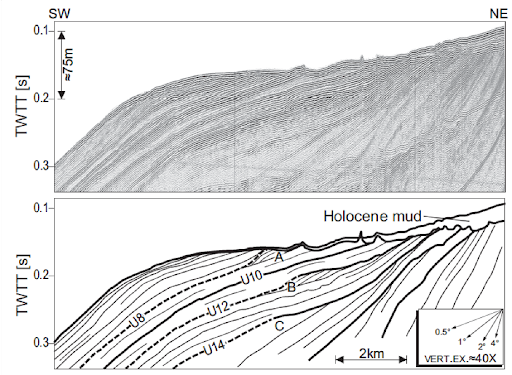 High-resolution seismic stratigraphy of Latium continental shelf. The basal unconformity underlying the highstan Holocene mud was formed during last sea level lowstand (MIS2) and following rise. Within the continental margin other Pleistocene unconformities are present, formed by 4th order glacioeustaic cycles (MIS 8, 10,12 e 14). Note subsidence increasing towards the shelf break and the presence of lowstand depositional terraces at paleo-shelf-breaks. |
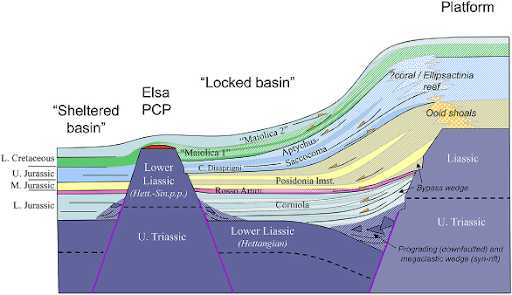 Cartoon depicting the buried northwestern margin of the Apulian Platform (Jurassic-Early Cretaceous). The existence of a pelagic carbonate platform (“Elsa PCP”) produced a confined basin, largely infilled with deposits shed by the active Apulian Platform. The intrabasinal high acted as a morphological “shield”, so that the basin behind it received no resedimented material and was dominated by purely pelagic sedimentation. |
The members of this Group cover a wide variety of research subjects, from geological mapping to carbonate geology, from paleoclimate reconstructions to the sequence stratigraphy of Quaternary successions, from turbidite deposits to the thermal evolution of sedimentary basins, to different fields of marine geology. |
|
Our Group includes scientific and organizational excellence encompassing two national coordinators of sections of the Italian Geological Society (“sedimentary geology” and “marine geology”), heads of Civil Protection Competence Centers, managers of national and international research projects, chairs of the most important international congresses in the field of sedimentary geology, organizers and leaders of Summer Schools in sedimentology for PhD students from around the world, and the direction of scientific journals (see personal CVs for further information). |
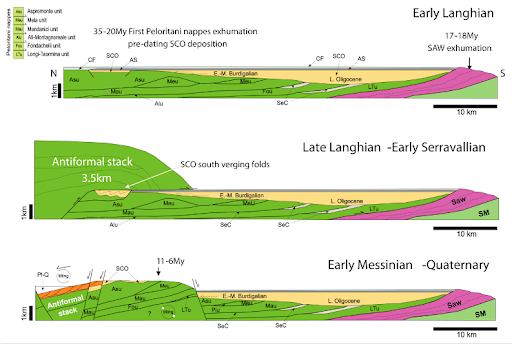 Schematic evolution of burial-exhumation of the Peloritani Mountains since the middle Miocene: (A) early Langhian; (B) late Langhian–(?)early Serravallian; (C) early Messinian–Quaternary. Acronyms: Pl-Q—Pliocene-Quaternary deposits; Ref—Reitano Flysch; SAW—Sicilide accretionary wedge; Sm—Serravallian-Messinian siliciclastic deposits; AS—Antisicilide unit; CF—Calcareniti di Floresta; SCO—Stilo-Capo d’Orlando Formation; Internal Zone (nappes from top to base): Asu—Apromonte unit; Meu—Mela unit; Piu—Piraino unit; Mau—Mandanici unit; Alu—Alì-Montagnareale unit; Fou—Fondachelli unit; LTu—Longi-Taormina unit. External Zone: SM—Sicilian Maghrebids |
|
Channelized turbidite deposits belonging to the Laga Formation (Upper Miocene, Central Apennines) |
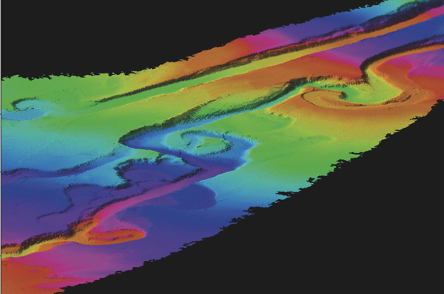
Submarine canyons of Gioia (right) and Mesima (left) on the Calabro-Tyrrhenian continental slope. Color cycles indicate water depth. The canyons join at 1,000 m w.d. Their course straight or with meanders is strictly controlled by the activity of faults affecting the continental margin. |
|
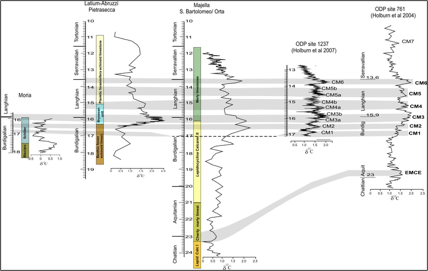
Comparison of the Miocene carbon isotope composition of shallow water sections (Latium-Abruzzi and Apula CarbonatePlatforms) and basinal sections (Umbria-Marche) plotted against stratigraphic depth and evidencing the Monterey isotope excursion; A) Moria section; B) Pietrasecca composite section; C) San Bartolomeo Valley-Orta river composite section. All the ages in the stratigraphic logs and related isotope curves have been calibrated with GTS 2004. The chronostratigraphic framework of the Moria section is from Di Stefano et al. (2015), based on biostratigraphy and magnetostratigraphy. The chronostratigraphic framework of the Pietrasecca section is provided by Sr isotope stratigraphy. The 87Sr⁄86Sr values of the samples have been converted to numerical ages using Version 4B: 08 ⁄ 04 of the Look-Up Table of Howarth & McArthur (1997). The stratigraphic framework of the San Bartolomeo-Orta river section is based on calcareous nannofossil data (after Brandano et al., 2016), referred to the stratigraphic scheme of Backmann et al. (2012). |